Walnuts for a Better Brain: Improve Cognitive Performance Naturally
For centuries, walnuts have held a place of honor, not just on dinner tables, but also in folklore and tradition. Their resemblance to the human brain is more than just a quirky coincidence; scientific evidence increasingly suggests that these wrinkled wonders offer a potent boost to cognitive function, acting as a natural ally in our quest for sharper minds and enhanced memory.
The Brain-Boosting Power of Walnuts: Unveiling the Science
The benefits of walnuts aren’t solely rooted in anecdotal evidence. Research points to a compelling synergy of nutrients within these nuts that contributes to brain health. This powerful combination includes:
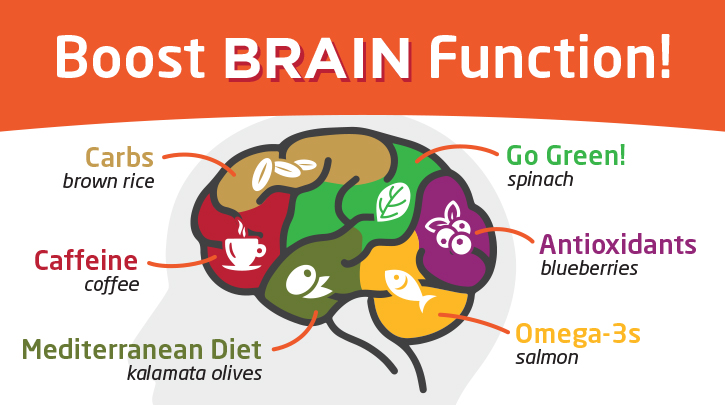
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids (particularly ALA): These essential fats are crucial for brain structure and function. They contribute to the integrity of cell membranes, support communication between brain cells, and even play a role in reducing inflammation, a factor linked to cognitive decline.
- Vitamin E: A potent antioxidant, vitamin E protects brain cells from damage caused by free radicals – unstable molecules that contribute to aging and neurodegenerative diseases. Walnuts are a significant source of alpha-tocopherol, the most biologically active form of vitamin E.
- Antioxidants: Beyond vitamin E, walnuts boast a rich array of other antioxidants, including polyphenols and melatonin. These compounds combat oxidative stress, shielding the brain from damage and promoting healthy aging.
- Fiber: The fiber in walnuts contributes to overall gut health, increasingly recognized as vital for brain health. A healthy gut microbiome can influence mood, cognitive function, and even protect against neuroinflammation.
- Melatonin: This hormone, crucial for regulating sleep-wake cycles, is also found in walnuts. Sufficient sleep is paramount for memory consolidation and optimal cognitive function.
Walnuts and Cognitive Performance: A Closer Look at the Research
Studies have linked walnut consumption to various cognitive improvements, including:
- Enhanced memory: Research suggests that regular walnut intake may improve memory recall and cognitive flexibility.
- Improved attention and focus: The nutrients in walnuts can support attention span and reduce mental fatigue.
- Better executive function: This encompasses higher-level cognitive processes like planning, problem-solving, and decision-making, all of which may benefit from walnut consumption.
- Reduced risk of cognitive decline: Some studies suggest a link between walnut consumption and a decreased risk of age-related cognitive decline and neurodegenerative diseases.
How to Incorporate Walnuts into Your Diet for Optimal Brain Health
Adding walnuts to your diet doesn’t require a complete overhaul. Here are some simple and delicious ways to incorporate these brain-boosting nuts:
- Snack on them plain: A handful of walnuts makes a satisfying and nutritious snack.
- Add them to salads: Walnuts add crunch and healthy fats to salads.
- Incorporate them into baked goods: Walnuts enhance the flavor and nutritional profile of muffins, cookies, and breads.
- Use them as a topping for yogurt or oatmeal: A sprinkle of walnuts adds texture and nutritional value.
- Make walnut milk: A healthy and delicious alternative to dairy milk.
Beyond the Brain: Additional Benefits of Walnuts
The benefits of walnuts extend beyond cognitive function. They’re also a good source of protein, fiber, and other essential nutrients that support overall health, including heart health and blood sugar control.
The Walnut Advantage: A Summary Table
| Benefit | Nutrient |
|---|---|
| Improved Memory | Omega-3s, Vitamin E |
| Enhanced Focus | Omega-3s |
| Reduced Inflammation | Omega-3s |
| Antioxidant Protection | Vitamin E, Polyphenols |
| Better Sleep | Melatonin |
Conclusion: Embrace the Power of the Walnut
Walnuts are more than just a delicious snack; they’re a powerhouse of nutrients that can significantly contribute to brain health and cognitive performance. By incorporating these versatile nuts into your diet, you can naturally support your cognitive function and embark on a journey towards a sharper, healthier mind.
Disclaimer: This article is for informational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. Consult with a healthcare professional before making any significant dietary changes, especially if you have underlying health conditions.

Additional Information
Walnuts for a Better Brain: A Deeper Dive into Cognitive Enhancement
The proposition that walnuts contribute to improved cognitive performance is gaining traction, but a nuanced understanding requires examining the underlying mechanisms and available evidence critically. While claims often highlight the “brain-shaped” nut as a whimsical analogy, the scientific basis rests on the rich composition of walnuts, specifically their concentration of omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidants, and other bioactive compounds.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids: The Foundation of Cognitive Health:
Walnuts are an excellent source of alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), an omega-3 fatty acid. ALA is an essential fatty acid, meaning the body cannot synthesize it and must obtain it through diet. While the body can convert ALA to eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) – omega-3s crucial for brain structure and function – the conversion rate is relatively low. Nevertheless, ALA’s presence contributes significantly to overall omega-3 status.
-
Mechanism of Action: DHA is a major structural component of brain cell membranes. Adequate DHA levels are linked to improved neuronal fluidity, impacting signal transmission and synaptic plasticity – the brain’s ability to adapt and learn. ALA, though less directly involved, contributes to the pool of precursors for DHA synthesis and may offer indirect neuroprotective benefits.
-
Evidence: Numerous studies have correlated higher omega-3 intake with improved cognitive function, particularly in older adults. For example, the PREDIMED study, a large-scale trial investigating the Mediterranean diet’s effect on cardiovascular health, showed that participants with higher adherence to the diet (rich in nuts, including walnuts) exhibited improved cognitive performance compared to the control group. However, directly attributing this solely to walnuts requires further research isolating the effects of this specific nut.
Antioxidants and Neuroprotection:
Walnuts boast a significant concentration of antioxidants, including vitamin E, melatonin, and polyphenols. These compounds combat oxidative stress, a major contributor to age-related cognitive decline and neurodegenerative diseases.
-
Mechanism of Action: Oxidative stress damages brain cells through the production of free radicals. Antioxidants neutralize these free radicals, protecting neurons from damage and potentially slowing the progression of age-related cognitive decline.
-
Evidence: In vitro and animal studies have demonstrated the neuroprotective effects of walnut extracts against oxidative stress-induced neuronal damage. However, translating these findings to human efficacy requires further robust clinical trials. While some human studies suggest a positive correlation between walnut consumption and reduced risk of cognitive decline, more research is needed to establish causality.
Other Bioactive Compounds:
Beyond omega-3s and antioxidants, walnuts contain other bioactive compounds potentially contributing to cognitive benefits:
- Vitamin B6: Crucial for neurotransmitter synthesis.
- Folate: Important for brain development and function.
- Magnesium: Plays a role in neuronal excitability and synaptic transmission.
- Zinc: Essential for various brain functions, including memory and learning.
Limitations and Considerations:
While the evidence suggests a potential link between walnut consumption and improved cognitive function, it’s crucial to acknowledge limitations:
- Correlation vs. Causation: Many studies demonstrate correlations, not definitive causation. Other dietary and lifestyle factors confound the results.
- Dosage and Consistency: The optimal daily intake of walnuts for cognitive benefit remains unclear. Consistent consumption is likely more important than sporadic high doses.
- Individual Variability: Individual responses to walnut consumption may vary based on genetics, pre-existing health conditions, and other lifestyle factors.
Conclusion:
Walnuts offer a rich profile of nutrients that support brain health. Their omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidants, and other bioactive compounds may contribute to improved cognitive performance, particularly in the context of a healthy lifestyle. However, while promising, the existing evidence warrants further research to establish clear causal relationships and determine optimal consumption levels for maximizing cognitive benefits. Integrating walnuts into a balanced diet, alongside other healthy lifestyle choices, remains a sensible approach to supporting overall cognitive well-being. Future research focusing on mechanistic studies and large-scale, well-controlled human trials is crucial for solidifying the role of walnuts in cognitive enhancement.
